Here is our the video compilation for the 2014 Science Film Festival! Enjoy.
Mrs. Tiday's Science Class
Pages
2013-2014
This year middle school science launches into a study of our physical world and its laws! Carlisle Christian Academy's 6th, 7th and 8th graders are learning about chemistry, waves, forces and electricity. We love to get our hands dirty and minds engaged with experiments and experiences. Join us here on our blog to see what we are doing in class! You can contact Mrs. Tiday at ctiday@carlislechristian.org.
Tuesday, June 3, 2014
Thursday, May 22, 2014
Science Animation Project 2014
For this project we will be using an animation app to model a scientific concept (Android or iPhone). Students will choose a topic and then design an animation that will illustrate it. We will have a Science Film Festival in class on the final day for students to share their work.
Here are 2 samples that I made as an illustration on my iPhone and an Android that a friend lent me:
Day
1 assignment: After watching the tutorials, create a simple animation
of a circle that falls from the sky to the ground. Mrs. Tiday should
see this before you begin your project.
NOTE: You cannot go back to an old frame and add a permanent feature SO be sure to add all permanent features the FIRST time the frame is opened.
Practice Day Assignment:
1. Open a new document
2. Erase the stick figure
3. On Frame #1 (the page you opened to) create a circle
4. Go to Frame #2, you should still see the circle. Move the circle down by grabbing the yellow dot.
5. Go to Frame #3, Move the circle again.
6. Play the frames by pushing the play button.
7. Now open a 4th frame and draw a square. (you should now have a circle and a square)
8. Open a 5th frame and move both the square and the circle.
9. Do this for a few more frames and then watch your movie.
10. When you have successfully created an animation for a circle and a square, you can begin to try out other parts of the program such as adjusting color, frame rate, line thickness and adding new stick people.
NOTE: You cannot go back to an old frame and add a permanent feature SO be sure to add all permanent features the FIRST time the frame is opened.
Science Concepts for Illustration (or choose your own)
1. The law of conservation of momentum, p. 357
2. Buoyancy, p.381
3. Bernoulli's Principle applied to airplanes, p. 395
4. Bernoulli's Principle applied to chimneys, p. 396
5. 1 type of simple machines at work, pp. 422-33
6. Covalent Bonding p. 167
7. How lightning forms
8. Series v/s Parallel Circuits
Here are 2 samples that I made as an illustration on my iPhone and an Android that a friend lent me:
Animation Creator (from iTunes, $1.99)...
Flip-a-Clip for Android (Free with ad)...
Vocabulary to discuss before we begin:
frame rate (fps)
onion skinning
backgrounds versus animated objects
looping
layers
copy and paste
For
this project the student will...
1.
Download
·
for iPhones: Animation
Creator from iTunes
·
for Android: Flip a
Clip from Google Play
2. Choose
a topic
3. Create
an animation (3 days in class)
A.
Approximately 20- 50
frames, 15 seconds
B.
The animation will be
free from distracting elements
C.
The animation will have
sufficient detail to present the topic clearly/accurately
D.
Name your file with
your first name and last initial (.mov if it asks you)
a.
example:
ctiday.mov
E.
The animation will be
emailed to ctiday@carlislechristian.org
4. Present
his/her animation at the Science Film Festival on the final day of the project
along with a verbal explanation of the scientific concept being
illustrated. (Test grade)
5. This is
a test grade; both the animation and the presentation (~1 min.) will count
toward the grade
6. If a
student forgets his device (or uses one in a way that does not support the goal
of the project or maintain the safety of the device) there will be an alternate
project assigned.
Getting started with
Animation Creator for iPhone/iPad
Basic intro, no sound
How to do layers
How to use a real photo as a template for an animation
Day 1 assignment: After watching the tutorials, create a simple animation of a circle that falls from the sky to the ground. Mrs. Tiday should see this before you begin your project.
NOTE: You cannot go back to an old frame and add a permanent feature SO be sure to add all permanent features the FIRST time the frame is opened.
NOTE: You cannot go back to an old frame and add a permanent feature SO be sure to add all permanent features the FIRST time the frame is opened.
Getting Started with
Flip-a-clip for Android
Review of the product and introduction:
Tutorial for basic flip-a-clip made by its creator:
Silent Flip-a-clip tutorial:
NOTE: You cannot go back to an old frame and add a permanent feature SO be sure to add all permanent features the FIRST time the frame is opened.
Getting Started with STYKZ.com
Free for computers
Practice Day Assignment:
1. Open a new document
2. Erase the stick figure
3. On Frame #1 (the page you opened to) create a circle
4. Go to Frame #2, you should still see the circle. Move the circle down by grabbing the yellow dot.
5. Go to Frame #3, Move the circle again.
6. Play the frames by pushing the play button.
7. Now open a 4th frame and draw a square. (you should now have a circle and a square)
8. Open a 5th frame and move both the square and the circle.
9. Do this for a few more frames and then watch your movie.
10. When you have successfully created an animation for a circle and a square, you can begin to try out other parts of the program such as adjusting color, frame rate, line thickness and adding new stick people.
NOTE: You cannot go back to an old frame and add a permanent feature SO be sure to add all permanent features the FIRST time the frame is opened.
Science Concepts for Illustration (or choose your own)
1. The law of conservation of momentum, p. 357
2. Buoyancy, p.381
3. Bernoulli's Principle applied to airplanes, p. 395
4. Bernoulli's Principle applied to chimneys, p. 396
5. 1 type of simple machines at work, pp. 422-33
6. Covalent Bonding p. 167
7. How lightning forms
8. Series v/s Parallel Circuits
Tuesday, May 20, 2014
Worksheet for CH 20, part 1
Middle School
Physical Science
CH 20 WS for Electricity, I and II
1.
What is static electricity? Electrons that have moved from one object to another, but do not keep flowing.
2.
What is electric current? Electrons that flow through a wire or other medium.
3.
When an electric current is flowing through a
wire… what is FLOWING? electrons
4.
How does an object become charged? When electrons move from one object to another and stay there, the object becomes negatively charged and the object they left becomes positively charged.
5.
Draw a picture of an electric field effecting
something:
6.
What are 3 ways that charge (electrons) can be
transferred? friction (rubbing), induction (through the air) and conduction (touching)
7.
Explain how lightning and electrons are related? the water droplets in the cloud rub together and the electrons move from one droplet to another. The cloud has more electrons on one side of it (negative) and less on the other (positive). The clouds wants to be balanced again and the negative side seeks out a positive area. The electrons jump from the negative part of the cloud to the positive area. This can be on the same cloud, on another cloud or on the ground.
8.
What is the word used to describe the number of
electrons that flow past a certain point per second? amps
9.
What is the word that describes the difference
in the electric charge from one side of a battery to the other? volts
10.
Name 2 conductors: silver, copper, aluminum and iron
11.
Name 2 insulators: glass, plastic, wood
12.
If a material holds its electrons tightly, is it
a conductor or an insulator? insulator
13.
If you need to slow down the flow of electrons
there are 4 ways to increase resistance.
What are they?
- lengthen the wire the electrons are flowing through
- increase the diameter (width) of the wire the electrons are flowing through
- increase the temperature
- use a material that holds more tightly to its electrons (less conductive material)
14.
Draw a circuit that includes 3 wires, a light, a battery and a dimmer
device.
Tuesday, April 29, 2014
Sound Ch 16: Review of roman numerals 3 and 4
Physical Science
Sound Ch 16
Review of roman numerals
3 and 4
1. If an auditorium is experiencing too much
reflection, what might the owner choose to do?
How would this help? The owner might want to add padding to the walls to absorb sound or add angles so that the sound reflects differently.
2. What
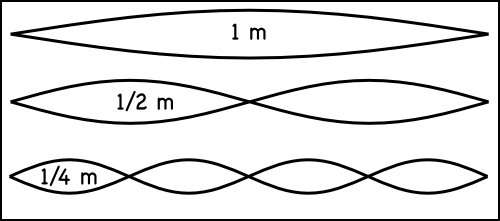
does this image represent in a sound wave? It is three of the same note begin played in different octaves.
3. What
is the difference between noise and music? Noises are random and music uses pitches whose waves are mathematically related.
4. Explain in a sentence how musical sound waves
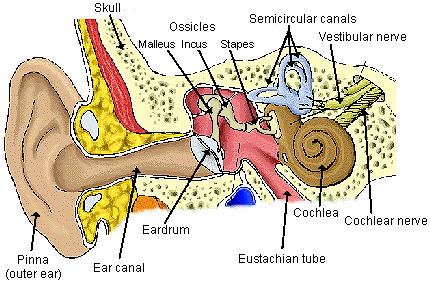
are able to be interpreted as music in
our brain. The outer ear funnel the sound wave to the eardrum. The movement of the drum triggers 3 small bones to move which transfers the vibration to the cochlea. The cochlea is full of fluid and 10,000 hairs. These hairs are connected to nerve cells which turn the movement into electrical impulses which are sent to the brain.
5. Draw
an ear and label the ear drum, the 3 small bones (called Ossicles in the picture), and the cochlea.
6. Name
2 causes of hearing loss. answers may vary, two possibilities are sudden loud noises like a lightening strike or sustained moderately loud sounds like a blender
7. What
are two changes to a normal ear that are common and cause hearing loss? a ruptured eardrum and dead hairs in the cochlea due to aging
8. Explain
what a hearing aid does (be specific and use information from our notes). A hearing aid can either increase the amplitude of all frequencies or it can target only certain frequencies.
9. Name
one use of sound waves that is not for music or noise. answer may vary, some possibilities are sonar and ultrasound
Thursday, April 17, 2014
Ch 15 WS Answers
Physical Science
Chapter 15
WS Characteristics of
Waves
1.
Define Wave: A disturbance that transfers energy from place to place
2.
What is the difference between a mechanical wave
and an electromagnetic wave? The mechanical wave must have a medium to pass through, but the electromagnetic does not need a medium.
3.
Give an example of each: Mech = sound wave; Electromagnetic = light wave
4.
Draw a wave and label the following parts:
crest, trough, amplitude, frequency, wavelength
(see our notes)
5.
Define the following
·
Amplitude - the distance from the center line to the crest
·
Frequency - the amount of crests to pass through a certain point per second
·
Wavelength - the distance from crest to crest
6.
Label the following as transverse or
longitudinal waves:
7.
Do compression and rarefaction occur in
transverse or longitudinal waves? Circle 3 compression sections
in the image above. (see where compression is labeled above)
8. We
learned one law of waves. It states that
the speed of a wave will stay constant as long as the wave
____continues to go through the same medium_________.
9. Does the law from #8 explain why music sounds
different when you are underwater and the music is above water? yes
10.
What
happens when a wave hits a medium that it cannot pass through? Give me the
scientific word. Reflection
11.
What happens when a wave hits a new (passable) medium
at an angle? Give me the scientific
word. Diffraction
12.
Give an example from everyday life when you have
seen this happen. In class we put a pencil in water and saw how it appears to be bent under the water. This is caused by the light waves bending as they pass through a new medium (water to glass to air).
13.
If two
waves hit each other (interference), there are two possible occurrences. What are they?
a. constructive interference
b. destructive interference
15.
Which of the two interferences will make the new
wave have twice the amplitude? constructive
16.
Interference sometimes leads to resonance. Give one example of resonance.
- a crystal glass breaking when a singer hits a note with the same frequency
- a building falling when an earthquake causes the dirt to have the same frequency as the building
- a bridge falling when the wind passing it has the same frequency
17.
EARTHQUAKES!!
Seismic waves are both transverse and longitudinal. They each travel
differently through the Earth. Which of
the two can be felt on the opposite side of our planet when there is an
earthquake? Longitudinal
18.
Why can’t the other one be felt on the other
side of the Earth? Because transverse waves cannot travel through a liquid and at least part of the Earth's core is a liquid.
19.
What does this tell us about the Earth’s core? At least part of it is a liquid
20.
Seismic
waves are called S or P
waves. Which one is the
longitudinal wave? P
21.
A
surface wave is another type of seismic wave.
These are very destructive and occur when____P or S waves reach the surface_________.
22.
We
detect earthquakes using a ____seismograph_____ and if we use 3 of these
instruments we can determine the ____location__ of the earthquake.
23.
What is one other use for a seismograph and
waves? It can be used to detect underground resources such as oil or water.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)